Surface activated bonding
Surface activated bonding (SAB) is a room temperature wafer bonding technology. In the standard SAB method, we first perform high-precision polishing on the bonding surface to obtain an extremely smooth and flat surface. The surface is bombarded with argon atoms in an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) state of 10-4-10-7 Pa to remove contaminants and native oxides adsorbed on the surface. Then, an intermediate layer is sputtered on the bonding surface to increase the bonding strength of the two substrates, and finally the bonding is completed at room temperature.
Our capabilities:
Bonding between most common semiconductor materials above 5mm
Processing flow:
Take the bonding of INP and INP materials as an example:
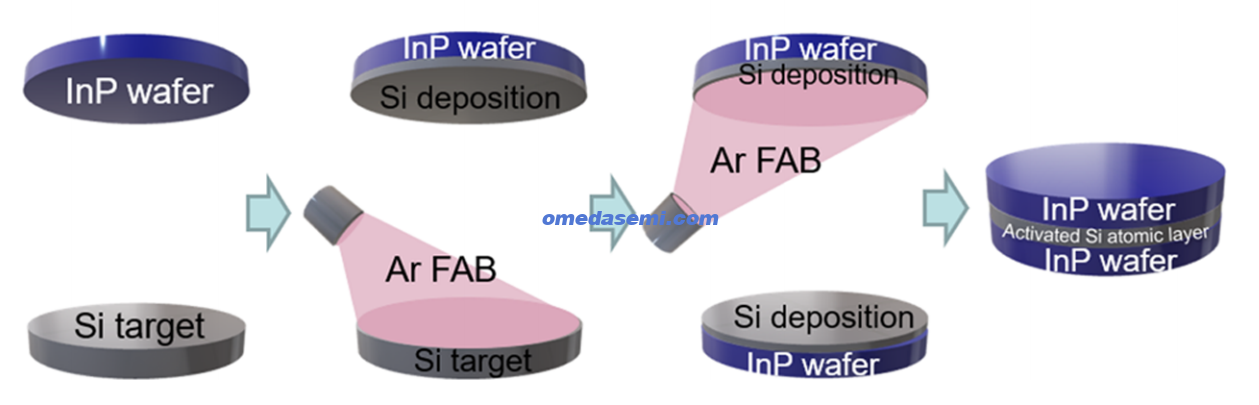
1. Polish the upper and lower surfaces to be bonded to a smooth and flat bondable surface (surface requirements as follows) through CMP and other processes
2. Deposit a modified layer on the INP substrate. The modified layer selected in this article is amorphous silicon
3. Bombard the surface to be bonded with Ar atoms under ultra-high vacuum to remove the oxide layer, water vapor layer, etc. on the surface to activate it
4. Bond at room temperature and obtain a successfully bonded composite substrate sheet with extremely high bonding strength and a large area of available area
Business process:
1. Fill in the surface conditions of the substrate to be bonded and put forward bonding requirements according to 
2. After we receive your processing order, we will evaluate the technical feasibility and conduct technical communication
3. After confirming the technical indicators and the acceptance criteria, provide a quotation
4. Sign the contract Processing is carried out in accordance with the acceptance standards
5. After processing, a shipping report with bonding strength and other data is provided
Key Features* Room temperature bonding
Since surface activated bonding uses argon atoms to bombard the surface to activate it first, and then adds a modified layer in the middle to enhance the bonding strength between the two, this bonding method does not require annealing and other processes, and can achieve high-strength bonding at room temperature
Features* Can achieve bonding of most materials
Different from conventional hydrophilic bonding, we use surface activated bonding technology. During bonding, a modified layer is added in the middle to match the upper and lower bonding surfaces. The material of the modified layer is generally amorphous silicon/aluminum oxide/titanium oxide. The middle layer can match the upper and lower materials and provide good bonding strength, so it can bond most semiconductor substrate materials.
Features* Interlayer(also called modified layer ) is needed
In order to increase the bonding strength, an intermediate layer, also called a modified layer, is often added between the two bonding interfaces. The material is generally amorphous silicon, aluminum oxide or titanium oxide
2. Surface activated bonding Generally, a modified layer is added between the upper and lower substrates of the bond. Generally, the optional materials are amorphous silicon, aluminum oxide (Al2o3) and titanium oxide (TiO2). Different modified layer materials can be selected in different application scenarios. For example, if you are doing surface activated bonding of photonic integrated circuits, such as SOI-LNOI, or manufacturing LNOI, or SICOI, we generally use Al2O3 as the modified layer, because aluminum oxide has a relatively good transmittance in the visible and near-infrared bands.
Features * Extremely high requirements for surface quality
because the bonding surface needs to be polished with high precision before bonding
Surface activated bonding can achieve bonding between most materials, but it should be noted that
1. Surface activated bonding has no strict restrictions on materials, but requires the bonding surface of the material to have a relatively good roughness and flatness
Surface shape requirements: TTV≤3μm; Bow≤25μm; Warp≤25μm
Surface roughness requirements:<0.5nm
Surface finish requirements: Particles greater than 0.3μm<10
Generally, the products after bonding need to be thinned and polished. In addition to bonding, we also provide a full set of ion implantation, thinning, and polishing services.
SICOI
LNOI
LTOI
SOI
Glass-glass bonding
Silicon-silicon bonding
Diamond-gallium nitride bonding
Silicon carbide-silicon carbide bonding
Lithium niobate crystal-silicon carbide bonding
Silicon carbide-silicon bonding
Lithium tantalate crystal-silicon carbide bonding
Diamond-indium phosphide bonding
Gallium arsenide-silicon carbide bonding
Diamond-silicon carbide bonding
Germanium-germanium bonding
Sapphire-sapphire bonding
Glass-silicon nitride bonding
Gallium arsenide-silicon carbide bonding
Indium phosphide-silicon carbide bonding
More materials-------
OMeda (Shanghai Omedasemi Co.,Ltd) was founded in 2021 by 3 doctors with more than 10 years of experience in nanpfabrication. It currently has 15 employees and has rich experience in nanofabrication (coating, lithography, etching, two-photon printing, bonding) and other processes. We support nanofabrication of 4/6/8-inch wafers.