Principle:
Electron beam evaporation is a thermal evaporation process that transfers more energy directly to the source material than thermal evaporation. This allows the deposition of materials with high melting temperatures, such as gold. In this method, the evaporation material is placed in a crucible or a water-cooled copper furnace and then heated by an electron beam. The heat causes the source material to evaporate and then deposit onto the substrate.
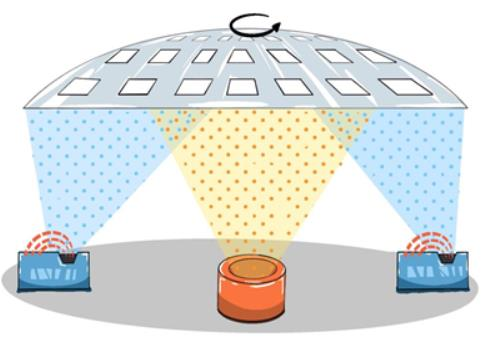
Processing Capabilities:
Metal films: Cr, Ti, Ni, Au, Al, Ag, Cu
Oxides: Sio2, Ti305, Ta2o5, Mgo, HfO2, MgF2
Applications: Optical coating, semiconductor coating
Supported size: 4-12 inches
Advantages:
A--Conventional models have high output, each furnace can produce 33 8-inch wafers
B--The modified coating equipment has a relatively high film uniformity of 1% on 8-inch wafers, and can produce 5 8-inch wafers
C--Suitable for a variety of materials, including those with high melting points that cannot be thermally evaporated
D--Provides better step coverage than sputtering or chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
E--Provides higher material utilization and higher deposition rate compared to sputtering
F--Compatible with a second ion assist source for pre-cleaning or ion-assisted deposition (IAD)
| Material | EBE | magnetron Sputtering | IBS | PECVD | ICPCVD | LPCVD | ALD | PLD | MOCVD | MBE |
| Au | O | O | ||||||||
| Ag | O | O | ||||||||
| Ta | O | |||||||||
| Al | O | O | ||||||||
| Cu | O | |||||||||
| Fe | O | |||||||||
| Mo | O | |||||||||
| Ti | O | O | ||||||||
| Ni | O | O | ||||||||
| W | O | |||||||||
| Ge | O | |||||||||
| Ir | O | |||||||||
| Zr | O | |||||||||
| Pt | O | O | ||||||||
| Cr | O | O | ||||||||
| NiCr | O | |||||||||
| TiW | O | |||||||||
| WC | O | |||||||||
| C | O | |||||||||
| NiSn | O | |||||||||
| AgSn | O | |||||||||
| AuSn | O | O | ||||||||
| MoS2 | O | |||||||||
| SIO2 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O |
| Ta2O5 | O | O | ||||||||
| TiO2 | O | O | O | |||||||
| GaO | O | |||||||||
| Ga2O3 | O | |||||||||
| Al2O3 | O | O | ||||||||
| IZO | O | |||||||||
| IGZO | O | |||||||||
| ITO | O | |||||||||
| CeO | O | |||||||||
| HfO2 | O | O | ||||||||
| NiO | O | |||||||||
| ZrO2 | O | O | O | |||||||
| Y2O3 | O | |||||||||
| WO3 | O | |||||||||
| MgO | O | O | O | |||||||
| GaN | O | |||||||||
| AlScN | O | |||||||||
| AlN | O | |||||||||
| TiN | O | |||||||||
| SiNX | O | O | ||||||||
| Si3N4 | O | O | O | |||||||
| SiC | O | |||||||||
| SiON | O | |||||||||
| Poly Si | O | |||||||||
| α Si | O | O | O | |||||||
| TEOS Sio2 | O | O | ||||||||
| SrTiO3 | O | |||||||||
| BaTiO3 | O | |||||||||
| MgF2 | O |
OMeda (Shanghai Omedasemi Co.,Ltd) was founded in 2021 by 3 doctors with more than 10 years of experience in nanpfabrication. It currently has 15 employees and has rich experience in nanofabrication (coating, lithography, etching, two-photon printing, bonding) and other processes. We support nanofabrication of 4/6/8-inch wafers.