Paper Download

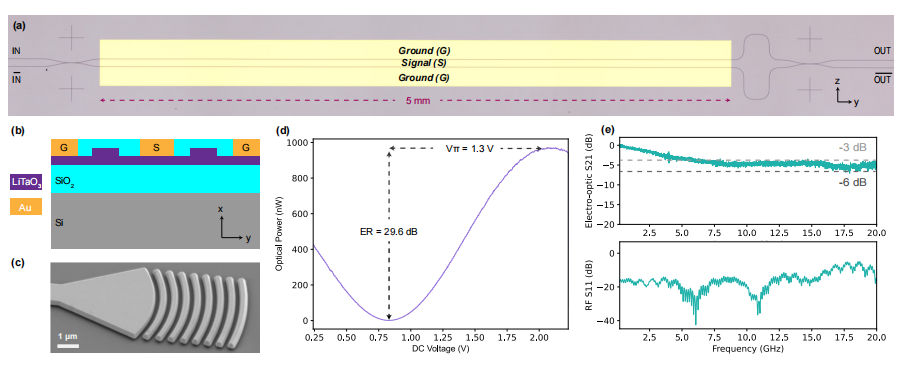
The paper discusses the development of a sub-volt near-infrared lithium tantalate (TFLT) electro-optic Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM), specifically designed for near-IR wavelengths, at 737 nm. The modulator exhibits excellent electro-optic performance, with a low half-wave voltage-length product of 0.65 V·cm, an extinction ratio of 30 dB, low optical loss of 5.3 dB, and a detector-limited bandwidth of 20 GHz. These performance characteristics are ideal for near-infrared opto-electronics applications, such as quantum information and spectroscopy.
The study also compares the TFLT MZM to thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) modulators, highlighting its superior DC bias stability. The TFLT MZM demonstrates less than 2 dB of laser power fluctuation over 16 minutes, significantly outperforming the TFLN MZM, which exhibits an 8 dB fluctuation under similar conditions. Furthermore, the optical loss coefficient for the TFLT waveguide is estimated to be 0.5 dB/cm at 638 nm.
In terms of fabrication, the device was produced using advanced techniques such as electron-beam lithography and inductively coupled plasma etching. Grating couplers were used for efficient coupling with optical fibers, and the modulator was carefully optimized to minimize optical loss.
Overall, the paper emphasizes the potential of TFLT-based electro-optic modulators for high-performance applications, offering a promising solution for integrating near-infrared modulation into a variety of optoelectronic devices.
OMeda (Shanghai Omedasemi Co.,Ltd) was founded in 2021 by 3 doctors with more than 10 years of experience in nanpfabrication. It currently has 15 employees and has rich experience in nanofabrication (coating, lithography, etching, two-photon printing, bonding) and other processes. We support nanofabrication of 4/6/8-inch wafers.