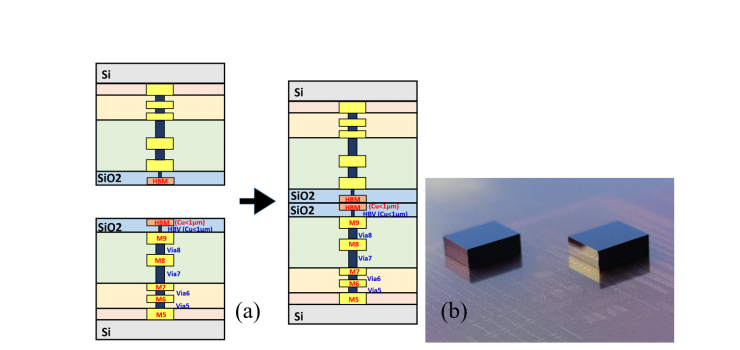
The article RF Performance of CMOS Technology Passive Devices Using 3D Hybrid Bonding Interconnections at mm-Wave Frequencies investigates the use of 3D hybrid bonding (3D-HB) for integrating passive components like transmission lines, inductors, capacitors, and transformers at millimeter-wave (mm-wave) frequencies up to 220 GHz. The study evaluates the impact of 3D-HB interconnections on these components, emphasizing their performance for high-frequency applications.
Key points from the paper include:
3D Hybrid Bonding Technology: The paper discusses the 3D-HB process, which enables the stacking of multiple integrated circuit layers to reduce interconnect lengths and improve overall system performance. This method provides more compact, efficient designs and is critical for enhancing electrical performance and minimizing power consumption in mm-wave devices.
Transmission Lines: Measurements show that transmission lines with 3D-HB interconnections exhibit very low insertion losses, less than 0.2 dB at 100 GHz, and up to 0.3 dB at 200 GHz. The study compares transmission lines with different numbers of 3D-HB transitions, demonstrating predictable and linear increases in loss with frequency. These results emphasize the efficiency of 3D-HB for high-frequency transmission.
Inductors: The 3D-HB integrated inductors demonstrate similar inductance values (around 200 pH) compared to 2D designs up to 100 GHz. However, at higher frequencies, the self-resonant frequency of the 3D inductor is slightly lower, and the quality factor (Q-factor) is reduced due to the parasitic effects of the 3D environment. These effects highlight the importance of addressing parasitics when designing 3D inductors for mm-wave applications.
Capacitors: The performance of 3D-HB capacitors is comparable to their 2D counterparts, maintaining stable capacitance values up to 50 GHz. However, at higher frequencies, the 3D-HB capacitors show a slight increase in equivalent series resistance (ESR), which is primarily attributed to the resistive effects introduced by the hybrid bonding connections. Despite this, the capacitors maintain a low ESR below 0.3 Ω up to 185 GHz.
Transformer Performance: The paper also explores the performance of a 3D transformer using 3D-HB interconnections, which achieves high inductive coupling up to 65 GHz. The transformer’s inductance and Q-factor measurements confirm the efficiency of 3D-HB for transformer applications, with mutual inductance reaching a maximum of 150 pH at 64 GHz and a coupling factor above 0.9.
Conclusion: The results confirm that 3D-HB technology enables efficient integration of passive components for mm-wave applications, with minimal performance degradation. Transmission lines, inductors, and capacitors perform well up to 150 GHz, and transformers show excellent inductive coupling. The study highlights the need for further optimization to mitigate parasitic effects at ultra-high frequencies, suggesting that 3D-HB is a promising solution for future mm-wave designs.
Overall, this work demonstrates that 3D-HB offers a viable path for creating compact, high-performance mm-wave devices, providing valuable insights into the integration of passive components for next-generation communication and computing systems.
OMeda (Shanghai Omedasemi Co.,Ltd) was founded in 2021 by 3 doctors with more than 10 years of experience in nanpfabrication. It currently has 15 employees and has rich experience in nanofabrication (coating, lithography, etching, two-photon printing, bonding) and other processes. We support nanofabrication of 4/6/8-inch wafers.