The article provides a comprehensive review of the state-of-the-art and outlooks of copper-to-copper (Cu-Cu) hybrid bonding (HB) technology, with a focus on its application in advanced semiconductor packaging. It covers various design, material, and process challenges, alongside a deep dive into the improvements made by major players such as Sony, Samsung, Applied Materials, and others. The study highlights key developments in bonding methods such as chip-on-chip (CoC), wafer-on-wafer (WoW), and their advanced derivatives like chip-on-wafer-on-wafer (CoWoW).
Key innovations discussed include:
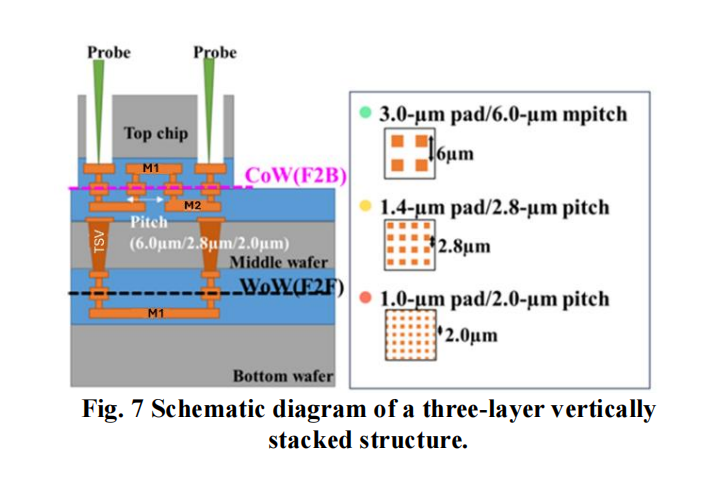
Hybrid Bonding Process Developments: Detailed explanations are provided on processes like wafer-level hybrid bonding and the use of fine-pitch Cu pads for efficient interconnects, alongside innovations in handling thin dies and minimizing voids.
Manufacturing Advances: Companies like Sony and Samsung have contributed significant research into optimizing hybrid bonding technologies, including the use of novel chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) methods and the integration of advanced materials like SiCN.
Reliability Testing: Various studies focus on the electrical and thermal performance of hybrid bonding under extreme conditions. The bonding strength, electromigration resistance, and mechanical properties of Cu-Cu hybrid joints are carefully evaluated, with a focus on scaling down to sub-micron levels.
Material Innovations: Nanocrystalline copper (NC-Cu) and improved passivation layers have been explored to enhance the stability of Cu bonds over time. Additionally, the use of SiCN as an interlayer dielectric material in bonding is gaining attention due to its improved performance in hybrid bonding scenarios.
Applications: The article highlights practical applications in 3D ICs, system-on-chip (SoC), and memory stacks, specifically focusing on developments in wafer-to-wafer (W2W) and die-to-wafer (D2W) bonding processes.
Overall, the research underscores how hybrid bonding technology is evolving to meet the demands of next-generation integrated circuits, with a focus on improving bonding accuracy, scalability, and thermal performance to support high-performance computing and memory systems.
OMeda (Shanghai Omedasemi Co.,Ltd) was founded in 2021 by 3 doctors with more than 10 years of experience in nanpfabrication. It currently has 15 employees and has rich experience in nanofabrication (coating, lithography, etching, two-photon printing, bonding) and other processes. We support nanofabrication of 4/6/8-inch wafers.